Reading Time: 5 minutes
As climate change gets worse, we’re paying more attention to pollution and the quality of our air. At the same time, lots of new technology like big data and the Internet of Things (IoT) is helping us use air quality data to monitor people’s health and guard our environment. But, how precise must this information be? This article looks at why air quality data is important, how it helps us make smart decisions, and other related topics.
Table of Contents
Understanding about Air Quality Data
What is Air Quality Data?
Air quality data (AQ data) is information measured and collected to detect the pollutants and air levels in a specific region. The data includes measurements of a wide range of pollutions in the air, such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other relevant indicators.
Which Data is Collected?
Based on the monitoring goals, local regulations, and the capabilities of monitoring stations, there are some differences in measuring level of air pollution data. However, some common pollutants are often measured:
Outdoor air pollutants include particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3). These come from emissions from combustion processes like burning fossil fuel, cooking, and heating burning activities, forest fires, or from industrial processes and household products.
Moreover, allergens such as pollen and moulds are also measured because they contribute to air pollution. The production from male organs of flowers creates pollen. In the reproductive process, it is carried by wind, insects, or other animals to reach the female part of other plants for fertilisation. Pollen is considered particulate. Therefore, some traditional air quality monitors can’t detect these particulates. To measure it and distinguish particulates like pollen from other pollutants, using a particulate unique-designed air quality sensor helps deliver accurate information.
Some biological contaminants in indoor air pollutants that present in homes, offices, and schools are commonly dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores; radon; tobacco smoke; bacteria, formaldehyde, and carbon monoxide.
Daily Air Quality Index (DAQI)
The DAQI provides a numerical value to identify the level of air pollution and is calculated based on the concentrations of various pollutants in the air. The index is divided into various bands that provide a description of the air quality.
The DAQI scale ranges from 1 to 10 and has been divided into four categories or levels of air quality: Low (1-3), Moderate (4-6), High (7-9) and Very High (10). If the DAQI value is high, it signifies that the level of air quality is poor, which can cause health concerns. For instance, a DAQI value of under 3 (Low) suggests little potential for air pollution. On the other hand, a DAQI value of 10 (Very High) signals serious concerns regarding air quality.
The DAQI system also includes advice for at-risk groups and the general population about what they should do in relation to outdoor activities when air pollution reaches certain levels, depending on whether they have any health conditions that might make them more vulnerable to air pollutants.
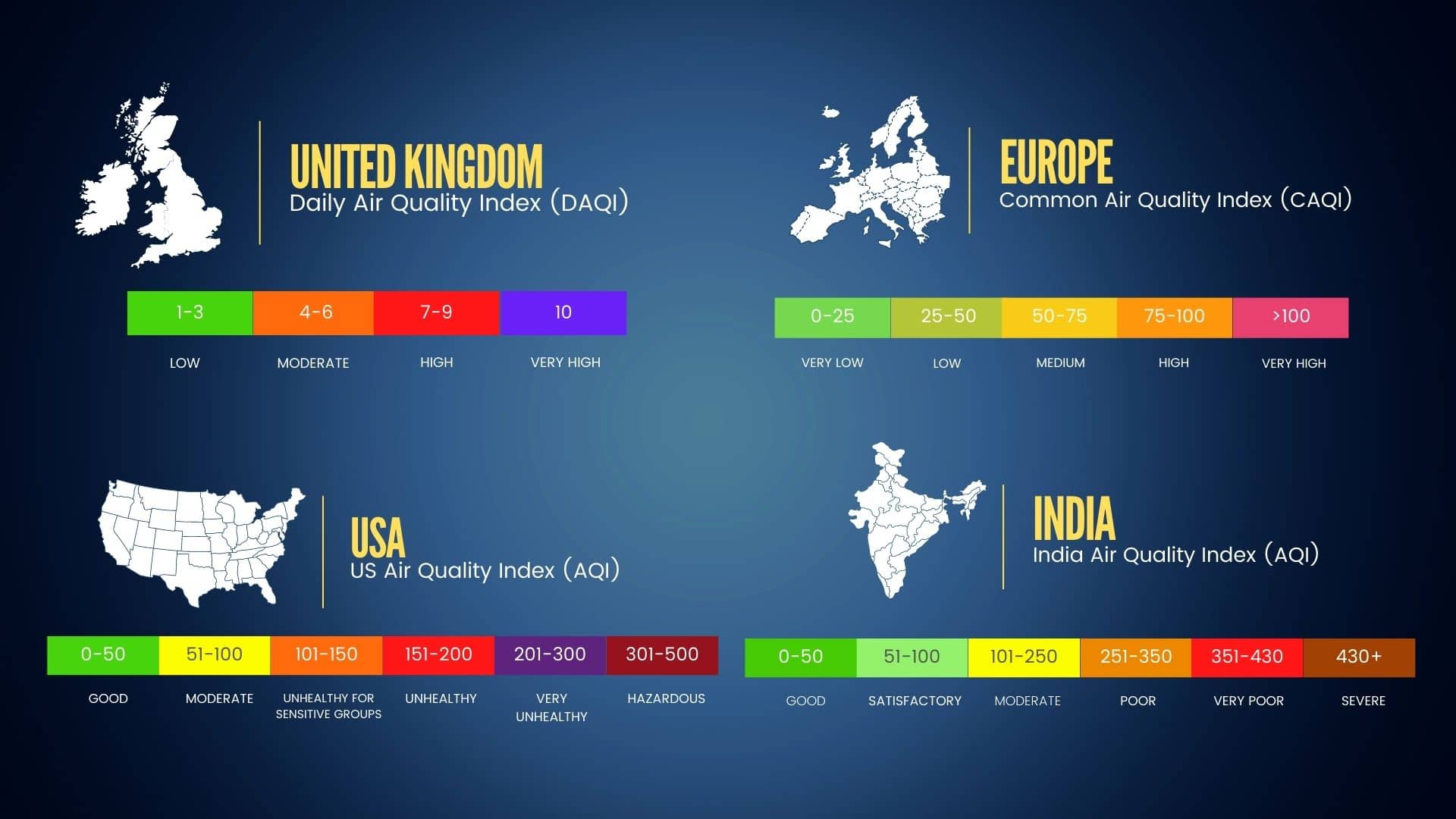
Different countries have different AQIs, with different point systems, and ways of calculating their pollution levels. This is in part due to different countries having different air quality problems, in which they need to focus on different pollutants.
How does Air Quality Data Work?
As we discuss a lot in some articles, how air quality monitoring works. You can read it in detail here.
Data is measured and collected from stations and low-cost sensors supported by IoT (5G, GMS, Wifi, etc). Air quality data is recorded and transmitted to a database or quality management system. It is then undergone quality assurance processes to ensure it is accurate and reliable. This process needs the involvement of data validation and quality controls. And what’s next?
Data is used to analyse and to identify the concentration levels of pollutants. This process may include some techniques like AI, machine learning, and algorithms used to help figure out patterns and forecasts. Some metrics are dominant pollutants, historical air quality data, pollution trends, and results for air quality levels from selected sensors. The air pollution analysis is visualised in user-friendly and real-time dashboards, websites, and mobile applications.
By interpreting air pollution data, it helps entities such as governments and policymakers to easily understand information and get actionable insights. This helps a smooth decision-making process. By doing so, they can implement measures and mitigation strategies.
Challenges of Air Quality Data
Lack of transparent data
Traditional air quality monitoring systems can’t collect comprehensive data. Moreover, there is a low level of data transparency. To gather these environmental data in various departments of separate units and make it available to the public through the proper channels, environmental protection departments typically need to invest in both people and material resources. As a result, it takes a lot of time and is impossible to thoroughly examine the validity and dependability of the data. Furthermore, the data will become meaningless for analysis purposes. Therefore, policymakers may make wrong decisions, which may hurt their further plans and strategies.
Significant gaps across air quality monitoring stations
Some areas or nations may not have an evenly distributed network of air quality monitoring stations. Monitoring stations are typically in urban areas or close to industrial locations. As a result, information about the quality of the air in these underdeveloped places may be insufficient or incomplete.
Moreover, it depends on station density. A higher density of stations enables a more comprehensive understanding of pollutants. In contrast, lower density may miss some important sources of pollution.
Low accuracy from some air quality sensors
Some stations rely on sensors to measure air pollution levels. So, lack of calibration, maintenance, and quality control procedures may lead to inaccurate and inconsistent readings. Moreover, as air quality monitoring technology is constantly developing. There are variations of some pollutants that become challenging to measure accurately. Some sensors measure certain pollutants, so they may miss capturing others, leading to the disparity in the understanding of overall air quality information.

Making Informed Decisions with Accurate Air Data Quality from Persium
Persium provides innovative and low-cost air quality solutions to help overcome the challenges mentioned above. So, how can Persium help?
- The Persium Pods have high-sensing capabilities for up to 12 major pollutants and the only sensor in the market with particulate shape detection for more accurate and detailed readings. In addition, data is securely transmitted to Persium’s cloud.
- Real-time dashboard where you can understand data patterns and prediction forecasts due to extended AI-driven.
- Persium’s API allows data to come from hyper-local networks of Persium Pods and other trusted sources globally. Moreover, you are always updated with real-time data, which is very helpful in standardised health recommendations.
By understanding air quality data and how it helps in making decisions, challenges it may face for better information, and Persium’s air quality solution, policymakers can empower the accurate air quality data to gain tangible and actionable insights, resulting in enhanced environmental health and mitigation plans.
Get ready for accurate and real-time air quality data. Request a demo with us to learn more!



